Exercises
1. Choose the right answer from the four alternatives given below.
(i) Which one of the following is not a plantation crop?
(a) Coffee
(b) Sugarcane
(c) Wheat
(d) Rubber
Answer - (c) Wheat
Answer - (c) Wheat
Note -
Option(C) is correct because wheat is not a plantation crop. Plantation crops are usually grown for profits. Wheat is a principal crop and worldwide staple food. It is grown on about 220 million hectares worldwide, covering more land area than any crop.
Option (A) is not correct because coffee is a plantation crop. It is traditionally grown in the Western Ghats. Now it is grown in Karnataka, Kerala and Tamilnadu. It is an export product with high employment content.
Option (B) is not correct because sugarcane is a plantation crop. It is grown in sub-tropical and tropical areas. It is mainly cultivated for sugar, but it is also grown for biofuel production.
Option (D) is not correct because rubber is a plantation crop. It is an important commercial product grown in Thailand, Malaysia and Indonesia. Rubber is used for making tires, mattresses etc.
Option (A) is not correct because coffee is a plantation crop. It is traditionally grown in the Western Ghats. Now it is grown in Karnataka, Kerala and Tamilnadu. It is an export product with high employment content.
Option (B) is not correct because sugarcane is a plantation crop. It is grown in sub-tropical and tropical areas. It is mainly cultivated for sugar, but it is also grown for biofuel production.
Option (D) is not correct because rubber is a plantation crop. It is an important commercial product grown in Thailand, Malaysia and Indonesia. Rubber is used for making tires, mattresses etc.
(ii) In which one of the following countries co-operative farming was the most successful experiment?
(a) Russia
(b) Denmark
(a) Russia
(b) Denmark
(c) India
(d) The Netherlands
Answer - (b) Denmark
Answer - (b) Denmark
Note -
Option (B) is correct because Denmark is the country where co-operative farming was the most successful experiment. Co-operative farming is an organisation where farmers remain the owner of his land individually, but farming is done jointly. In Denmark, the movement was so successful that every farmer becomes member of a co-operative.
Option (A) is not correct because Russia focused more on collective farming. Collective farming is based on social ownerships. It was introduced in erstwhile Soviet Union.
Option (C) is not correct because in India different types of farming are practised such as shifting agriculture, subsistence agriculture etc. Co-operative farming failed in India because all farmers are not agreed to grow same crop. Farmers expect more shares in profits compared to others.
Option (D) is not correct because in Netherland co-operative farming was practised but not so successful as compared to Denmark.
Option (A) is not correct because Russia focused more on collective farming. Collective farming is based on social ownerships. It was introduced in erstwhile Soviet Union.
Option (C) is not correct because in India different types of farming are practised such as shifting agriculture, subsistence agriculture etc. Co-operative farming failed in India because all farmers are not agreed to grow same crop. Farmers expect more shares in profits compared to others.
Option (D) is not correct because in Netherland co-operative farming was practised but not so successful as compared to Denmark.
(iii) Growing of flowers is called:
(a) Truck farming
(b) Factory farming
(a) Truck farming
(b) Factory farming
(c) Mixed farming
(d) Floriculture
Answer - (d) Floriculture
Option (A) is not correct because truck farming is related to production of vegetables.
Option (B) is not correct because factory farming is related to raising large numbers of animals for foods.
Option (C) is not correct because mixed farming involves the growing of crops as well as the raising of livestock.
(iv) Which one of the following types of cultivation was developed by European colonists?
(a) Kolkoz
(b) Viticulture
Answer - (d) Floriculture
Note -
Option (D) is correct because growing of flower is called floriculture. It is the branch of horticulture. Floriculture is not only related to cultivation of flowers, but it is also related to cultivation of ornamental plants for gardens.Option (A) is not correct because truck farming is related to production of vegetables.
Option (B) is not correct because factory farming is related to raising large numbers of animals for foods.
Option (C) is not correct because mixed farming involves the growing of crops as well as the raising of livestock.
(iv) Which one of the following types of cultivation was developed by European colonists?
(a) Kolkoz
(b) Viticulture
(c) Mixed farming
(d) Plantation
Answer - (d) Plantation
Option (A) is not correct because Kolkhoz was introduced in Soviet Union to improve the methods of agriculture.
Option (B) is not correct because viticulture was developed by Phoenicians which were later used in Carthage.
Option (C) is not correct because mixed farming was found in developed parts of world such as Northwestern Europe, Eastern North America, and parts of Eurasia.
Answer - (d) Plantation
Note -
Option (D) is correct because plantation was developed by European colonists. Plantations farming require large capital investment, managerial and technical support.Option (A) is not correct because Kolkhoz was introduced in Soviet Union to improve the methods of agriculture.
Option (B) is not correct because viticulture was developed by Phoenicians which were later used in Carthage.
Option (C) is not correct because mixed farming was found in developed parts of world such as Northwestern Europe, Eastern North America, and parts of Eurasia.
(v) In which one of the following regions is extensive commercial grain cultivation not practised?
(a) American Canadian prairies
(b) European Steppes
(a) American Canadian prairies
(b) European Steppes
(c) Pampas of Argentina
(d) Amazon Basin
Answer - (d) Amazon Basin
Option (A) is not correct because American Canadian prairies experience dry semi-arid climates with an annual precipitation of 12 to 15 inches which is suitable for commercial grain cultivation.
Option (B) is not correct because European steppes are the largest temperate steppe and experience semi-arid climate which is best for commercial grain cultivation.
Option (C) is not correct because Pampas of Argentina is also semi-arid region. Wheat is Argentina’s largest crop in harvested land area.
Answer - (d) Amazon Basin
Note -
Option (D) is correct because Amazon Basin is the region where extensive commercial grain cultivation is not practised. Commercial grain cultivation is practised in the interior parts of semi-arid lands of the mid latitudes. Amazon Basin is the largest tropical forest in the world. People practise shifting cultivation here.Option (A) is not correct because American Canadian prairies experience dry semi-arid climates with an annual precipitation of 12 to 15 inches which is suitable for commercial grain cultivation.
Option (B) is not correct because European steppes are the largest temperate steppe and experience semi-arid climate which is best for commercial grain cultivation.
Option (C) is not correct because Pampas of Argentina is also semi-arid region. Wheat is Argentina’s largest crop in harvested land area.
(vi) In which of the following types of agriculture is the farming of citrus fruit very important?
(a) Market gardening
(b) Plantation agriculture
(a) Market gardening
(b) Plantation agriculture
(c) Mediterranean agriculture
(d) Co-operative farming
Answer - (c) Mediterranean agriculture
Option (A) is not correct because market gardening is related to cultivation of high valuable crops such as vegetables, fruits and flowers.
Option (B) is not correct because plantation agriculture is mainly done for profits. Example of plantation crops are tea, coffee, cocoa etc.
Option (D) is not correct because in co-operative farming group of farmers form a society by pooling in their resources for more efficient and profitable farming.
Answer - (c) Mediterranean agriculture
Note -
Option (C) is correct because in Mediterranean agriculture the farming of citrus fruit is very important. Southwestern parts of South Africa, Southern California and southwestern parts of Australia are important supplier of citrus fruits.Option (A) is not correct because market gardening is related to cultivation of high valuable crops such as vegetables, fruits and flowers.
Option (B) is not correct because plantation agriculture is mainly done for profits. Example of plantation crops are tea, coffee, cocoa etc.
Option (D) is not correct because in co-operative farming group of farmers form a society by pooling in their resources for more efficient and profitable farming.
(vii) Which one type of agriculture amongst the following is also called ‘slash and burn agriculture’?
(a) Extensive subsistence agriculture
(b) Primitive subsistence agriculture
(c) Extensive commercial grain cultivation
(d) Mixed farming
Answer - (b) Primitive subsistence agriculture
Option (A) is not correct because extensive subsistence agriculture is practised in moderately populated region, and it is practised in large farms with relatively lower inputs.
Option (C) is not correct because extensive commercial grain cultivation is the cultivation of principal crop such as wheat and also other crops like corn, barley etc. It is practised in semi-arid region.
Option (D) is not correct because mixed farming is also known as polyculture. It is a system of farming which involves the growing of crops as well s the raising of livestock.
(viii) Which one of the following does not follow monoculture?
(a) Dairy farming
(b) Mixed farming
(a) Extensive subsistence agriculture
(b) Primitive subsistence agriculture
(c) Extensive commercial grain cultivation
(d) Mixed farming
Answer - (b) Primitive subsistence agriculture
Note -
Option (B) is correct because primitive subsistence agriculture is also slash and burn agriculture. It is widely practised by many tribes in the tropics especially in Africa, southeast Asia.Option (A) is not correct because extensive subsistence agriculture is practised in moderately populated region, and it is practised in large farms with relatively lower inputs.
Option (C) is not correct because extensive commercial grain cultivation is the cultivation of principal crop such as wheat and also other crops like corn, barley etc. It is practised in semi-arid region.
Option (D) is not correct because mixed farming is also known as polyculture. It is a system of farming which involves the growing of crops as well s the raising of livestock.
(viii) Which one of the following does not follow monoculture?
(a) Dairy farming
(b) Mixed farming
(c) Plantation agriculture
(d) Commercial grain farming
Answer - (b) Mixed farming
Option (A) is not correct because dairy farming is monoculture. It is a type of agriculture for production of milk.
Option (C) is not correct because plantation agriculture is the cultivation of cash crops.
Option (D) is not correct because commercial grain farming is an extensive and mechanised form of agriculture in which we mainly cultivate grain.
2. Answer the following questions in about 30 words.
(i) Future of shifting cultivation is bleak. Discuss.
Answer - Shifting cultivation is also called slash and burn agriculture. It is an agricultural system in which a person uses a piece of land, cut trees and clear the land for cultivation. They burn the uprooted trees and mix their ashes in the soil so as to fertile the soil. After cultivation and harvesting they move on to other land and repeat the process. Future of shifting cultivation is bleak because this has resulted in large scale deforestation and increases soil infertility.
(ii) Market gardening is practised near urban areas. Why?
Answer - Market gardening is the production of fruits, vegetables and flowers as cash crops on relatively small scales and sold directly to consumers. It is both labour and capital intensive. It is practised near urban areas because there is good transportation links with urban centre and high group of consumers are located. It is mainly practised there for more and more profit.
(iii) Large scale dairy farming is the result of the development of transportation and refrigeration.
Answer - Dairy farming is a type of agriculture that is focused on producing milk. Milk can be used to produce dairy products such as cheese, ghee etc. It is highly labour and capital intensive. Large scale dairy farming is the result of the development of transportation and refrigeration because dairy products require quick and suitable transportation as these items are perishable and refrigeration have increased the duration of storage of these products.
3. Answer the following questions in not more than 150 words.
(i) Differentiate between Nomadic Herding and Commercial Livestock Rearing.
Answer -
Pastoral nomadism is associated with three important regions. The core region extends from the Atlantic shores of North Africa eastwards across the Arabian Peninsula into Mongolia and Central China. The second region extends over the tundra region of Eurasia. In the southern hemisphere there are small areas in South-west Africa and on the island of Madagascar.
Movement in search of pastures is undertaken either over vast horizontal distances or vertically from one elevation to another in the mountainous regions. The process of migration from plain areas to pastures on mountains during summers and again from mountain pastures to plain areas during winters is known as transhumance. In mountain regions, such as Himalayas, Gujjars, Bakarwals, Gaddis and Bhotiyas migrate from plains to the mountains in summers and to the plains from the high-altitude pastures in winters. Similarly, in the tundra regions, the nomadic herders move from south to north in summers and from north to south in winters.
The number of pastoral nomads has been decreasing and the areas operated by them shrinking. This is due to (a) imposition of political boundaries; (b) new settlement plans by different countries.
Commercial Livestock Rearing
Unlike nomadic herding, commercial livestock rearing is more organised and capital intensive. Commercial livestock ranching is essentially associated with western cultures and is practised on permanent ranches. These ranches cover large areas and are divided into a number of parcels, which are fenced to regulate the grazing. When the grass of one parcel is grazed, animals are moved to another parcel. The number of animals in a pasture is kept according to the carrying capacity of the pasture.
This is a specialised activity in which only one type of animal is reared. Important animals include sheep, cattle, goats and horses. Products such as meat, wool, hides and skin are processed and packed scientifically and exported to different world markets.
Rearing of animals in ranching is organised on a scientific basis. The main emphasis is on breeding, genetic improvement, disease control and health care of the animals. New Zealand, Australia, Argentina, Uruguay and United States of America are important countries where commercial livestock rearing is practised.
(ii) Discuss the important characteristic features of plantation agriculture. Name a few important plantation crops from different countries.
Visit a nearby village and observe the cultivation of some crops. Ask the farmers and list the various operations.
Answer - (b) Mixed farming
Note -
Option (B) is correct because mixed farming does not follow monoculture. Monoculture is the production of single crop or raising of single livestock. Mixed farming involves the growing of crops as well as the raising of livestock.Option (A) is not correct because dairy farming is monoculture. It is a type of agriculture for production of milk.
Option (C) is not correct because plantation agriculture is the cultivation of cash crops.
Option (D) is not correct because commercial grain farming is an extensive and mechanised form of agriculture in which we mainly cultivate grain.
2. Answer the following questions in about 30 words.
(i) Future of shifting cultivation is bleak. Discuss.
Answer - Shifting cultivation is also called slash and burn agriculture. It is an agricultural system in which a person uses a piece of land, cut trees and clear the land for cultivation. They burn the uprooted trees and mix their ashes in the soil so as to fertile the soil. After cultivation and harvesting they move on to other land and repeat the process. Future of shifting cultivation is bleak because this has resulted in large scale deforestation and increases soil infertility.
(ii) Market gardening is practised near urban areas. Why?
Answer - Market gardening is the production of fruits, vegetables and flowers as cash crops on relatively small scales and sold directly to consumers. It is both labour and capital intensive. It is practised near urban areas because there is good transportation links with urban centre and high group of consumers are located. It is mainly practised there for more and more profit.
(iii) Large scale dairy farming is the result of the development of transportation and refrigeration.
Answer - Dairy farming is a type of agriculture that is focused on producing milk. Milk can be used to produce dairy products such as cheese, ghee etc. It is highly labour and capital intensive. Large scale dairy farming is the result of the development of transportation and refrigeration because dairy products require quick and suitable transportation as these items are perishable and refrigeration have increased the duration of storage of these products.
3. Answer the following questions in not more than 150 words.
(i) Differentiate between Nomadic Herding and Commercial Livestock Rearing.
Answer -
Nomadic herding or pastoral nomadism is a primitive subsistence activity, in which the herders rely on animals for food, clothing, shelter, tools and transport. They move from one place to another along with their livestock, depending on the amount and quality of pastures and water. Each nomadic community occupies a well-identified territory as a matter of tradition.
A wide variety of animals is kept in different regions. In tropical Africa, cattle are the most important livestock, while in Sahara and Asiatic deserts, sheep, goats and camel are reared. In the mountainous areas of Tibet and Andes, yak and lamas and in the Arctic and sub-Arctic areas, reindeer are the most important animals.
A wide variety of animals is kept in different regions. In tropical Africa, cattle are the most important livestock, while in Sahara and Asiatic deserts, sheep, goats and camel are reared. In the mountainous areas of Tibet and Andes, yak and lamas and in the Arctic and sub-Arctic areas, reindeer are the most important animals.

Reindeering in the northen regions of Alaska where most of the Eskimos own about two third of the stock.
Pastoral nomadism is associated with three important regions. The core region extends from the Atlantic shores of North Africa eastwards across the Arabian Peninsula into Mongolia and Central China. The second region extends over the tundra region of Eurasia. In the southern hemisphere there are small areas in South-west Africa and on the island of Madagascar.
Movement in search of pastures is undertaken either over vast horizontal distances or vertically from one elevation to another in the mountainous regions. The process of migration from plain areas to pastures on mountains during summers and again from mountain pastures to plain areas during winters is known as transhumance. In mountain regions, such as Himalayas, Gujjars, Bakarwals, Gaddis and Bhotiyas migrate from plains to the mountains in summers and to the plains from the high-altitude pastures in winters. Similarly, in the tundra regions, the nomadic herders move from south to north in summers and from north to south in winters.
The number of pastoral nomads has been decreasing and the areas operated by them shrinking. This is due to (a) imposition of political boundaries; (b) new settlement plans by different countries.
Commercial Livestock Rearing
Unlike nomadic herding, commercial livestock rearing is more organised and capital intensive. Commercial livestock ranching is essentially associated with western cultures and is practised on permanent ranches. These ranches cover large areas and are divided into a number of parcels, which are fenced to regulate the grazing. When the grass of one parcel is grazed, animals are moved to another parcel. The number of animals in a pasture is kept according to the carrying capacity of the pasture.
This is a specialised activity in which only one type of animal is reared. Important animals include sheep, cattle, goats and horses. Products such as meat, wool, hides and skin are processed and packed scientifically and exported to different world markets.
Rearing of animals in ranching is organised on a scientific basis. The main emphasis is on breeding, genetic improvement, disease control and health care of the animals. New Zealand, Australia, Argentina, Uruguay and United States of America are important countries where commercial livestock rearing is practised.
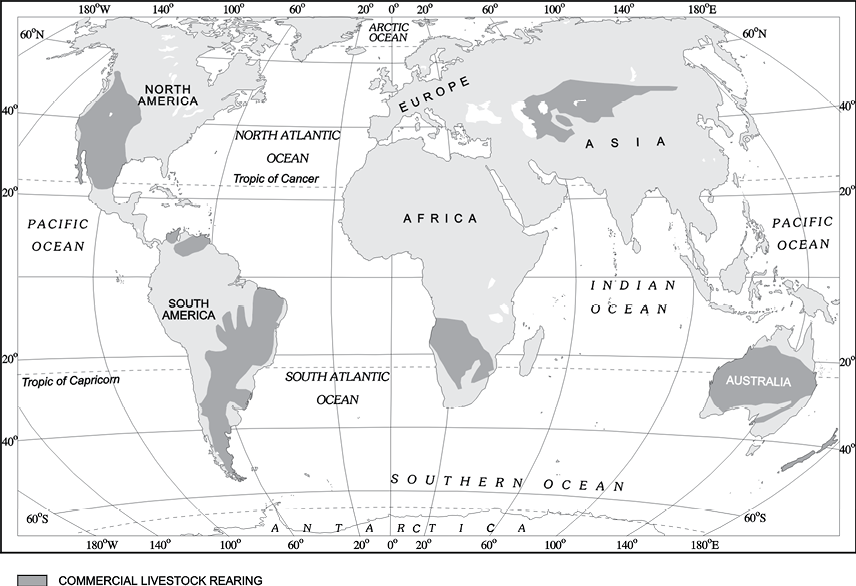 |
| Commercial Livestock Rearing |
(ii) Discuss the important characteristic features of plantation agriculture. Name a few important plantation crops from different countries.
Answer - Plantation agriculture was introduced by the Europeans in colonies situated in the tropics. Some of the important plantation crops are tea, coffee, cocoa, rubber, cotton, oil palm, sugarcane, bananas and pineapples. Plantation agriculture is a form of commercial farming where crops are grown on large land area. These crops are grown for profit. Plantation crops are also known as cash crop.
The characteristic features of this type of farming are large estates or plantations, large capital investment, managerial and technical support, scientific methods of cultivation, single crop specialisation, cheap labour, and a good system of transportation which links the estates to the factories and markets for the export of the products. The important characteristic features of plantation agriculture are:
*It requires scientific methods of cultivation.
*It is both labour intensive and capital intensive.
*Crops are mainly grown for market.
*Large capital investment is done.
*It is a single crop farming practised on a large area.
*A good system of transportation which links the estates to the factories and markets for the exports of the products play an important role in development of plantation.
*Managerial and technical support helps in development of plantation.
*It requires scientific methods of cultivation.
*It is both labour intensive and capital intensive.
*Crops are mainly grown for market.
*Large capital investment is done.
*It is a single crop farming practised on a large area.
*A good system of transportation which links the estates to the factories and markets for the exports of the products play an important role in development of plantation.
*Managerial and technical support helps in development of plantation.
Few important plantation crops from different countries are:
The French established cocoa and coffee plantations in west Africa. The British set up large tea gardens in India and Sri Lanka (The slopes of hills are used for tea plantations because of favourable geographical conditions.), rubber plantations in Malaysia and sugarcane and banana plantations in West Indies. Spanish and Americans invested heavily in coconut and sugarcane plantations in the Philippines. The Dutch once had monopoly over sugarcane plantation in Indonesia. Some coffee fazendas (large plantations) in Brazil are still managed by Europeans.
Project/Activity
Visit a nearby village and observe the cultivation of some crops. Ask the farmers and list the various operations.
